Thyroid, Salivary Gland & Sialendoscopy Conditions
Thyroid, Salivary Gland & Sialendoscopy Procedures
Salivary Stones
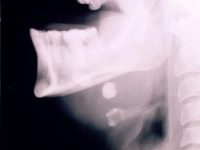
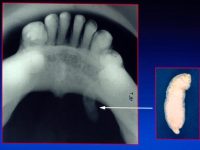
Sialolithiasis causes obstruction of salivary outflow from the glands due to presence of stones in the outflow tract. This happens mostly in patients in fourth or fifth decade of life with poor oral hygiene. Sialolithiasis contributes to 25% of all salivary gland pathology.
At Adventis ENT clinic we offer comprehensive treatment for salivary gland stones facilitating the advance technology for diagnosis and treatment.
What are Salivary Stones ?
Sialoliths or salivary stones are calcified, grainy, or stony concretions in the salivary glands causing obstructive or inflammatory conditions of the gland (sialolithiasis).
Mostly affects submandibular glands (84%) followed by parotid glands (13%); the stones are found in the ducts of submandibular glands more commonly and the stones are localised mostly in the salivary tissue of parotids.
What are the common symptoms of Salivary Stones ?
- Pain and Swelling of the affected gland occurring during mealtimes.
- Fever may or may not be present.
- Please note that 1% to 5% of salivary stones do not produce symptoms.
How do we diagnose Salivary Stones ?
The persons typical history is usually suggestive. We carry out a detailed examination and often the stones can be felt by the ENT Surgeon.
In order to conform the diagnosis , we may ask for imaging investigations. These can be one or more of : Ultrasonography of the glands to locate stones , intraoral occlusal X-ray , or finally CT and Cone Beam CT Scans.
Some stones are not Radio-Opaque ( ie . they are not seen on X-Ray or CT scans). In these situations we may suggest an investigation called Sialography. This is done for evaluating suspected parotid gland stones with almost 100% detection rates.
How do we treat Salivary Stones?
The principle of treatment is removal of stone while preserving glandular function and causing least number of complications.
Non invasive methods include the Use of salivation enhancing agents such as lemon drops and chewable vitamin c tablets, local massage, irrigation of the salivary duct with steroids with or without antibiotics, and anti inflammatory medications.
We deliver minimally invasive technique of Sialendoscopy. In this we use miniature and fine endoscope inserted in to the duct to examine the inside and use fine instrumentation to remove them through the duct itself.
Stones lying in the duct can easily be removed under local anaesthesia by opening the duct itself.
Extra Corporeal Shock Wave: Lithotripsy is a technique used for large stones to be broken down into smaller bits using ultra sonic shock waves and allow them to pass out spontaneously.
Finally , if the stones are embedded in the gland itself, then this will require surgical removal of the gland itselfalong with the stone, under general anaesthesia.
You can prevent stone formation by maintaining proper oral hygiene and staying well hydrated

